AMTI Latest News
March 2023
Natural language processing, a form of AI, devours all the text in countless pages of healthcare documents to help health IT experts in the U.S. military do their job more efficiently.
January 2023
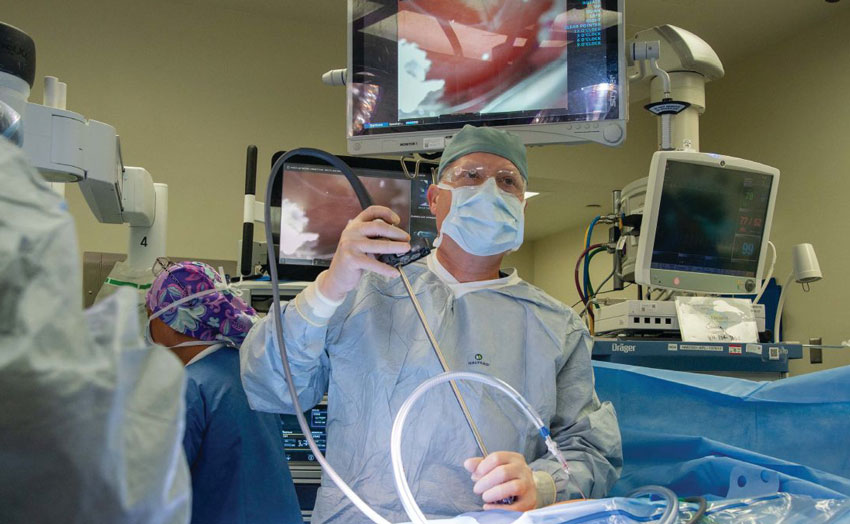
Championed by Naval Medical Center-San Diego’s Virtual Medical Operations Center (VMOC), a relatively new, communications-based, autonomy-facilitative practice enabling remote telementoring to boost operational surgical capability.
September 2021
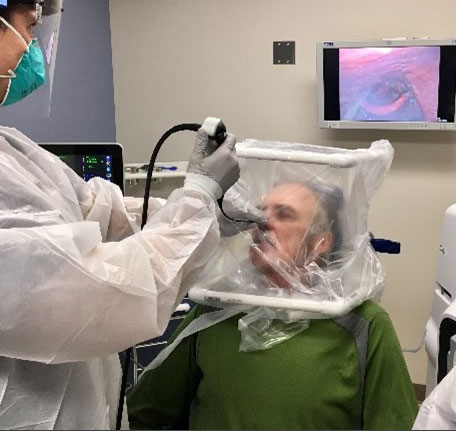
COVID-19 has drastically changed the world. Its airborne spread and prolonged, silent transmission have wreaked havoc on an unprepared enterprise - the military was no exception. During the early phases of the outbreak, hospitals struggled to increase personal protective equipment (PPE), and frequent exposures decreased the number of available healthcare workers. This threat remains as novel variants cycle through populations.

Many, many thanks to the TATRC leadership for championing the AMTI program! Initially managed by Mr. John Winston, and now Ms. Holly Pavliscsak, this program has had a remarkable impact on the Baylor University-Keller Army Community Hospital Division 1 Sports Physical Therapy Fellowship at West Point, NY, and has taught our team, and me personally, very much over the last 7+ years.
June 2021
A majority of military Service Members are overweight or obese and are not meeting physical fitness goals, leading to increased health care costs and days of lost work per year.
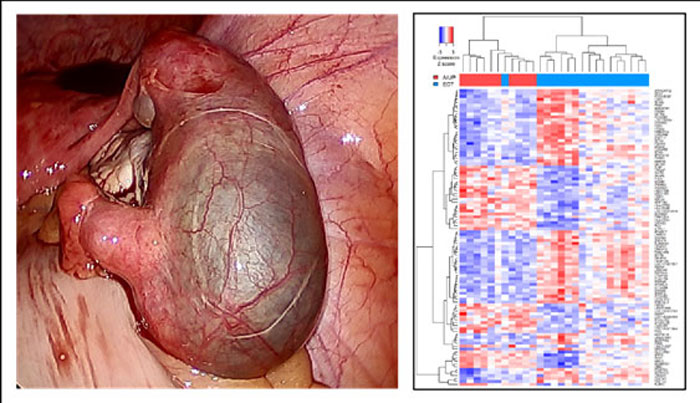
Did you know that nearly 16% of active component U.S. military members are women, and the majority are reproductive age? As the number of military servicewomen and their operational scope increase, it is important to understand and mitigate health issues that uniquely impact female servicemember readiness.
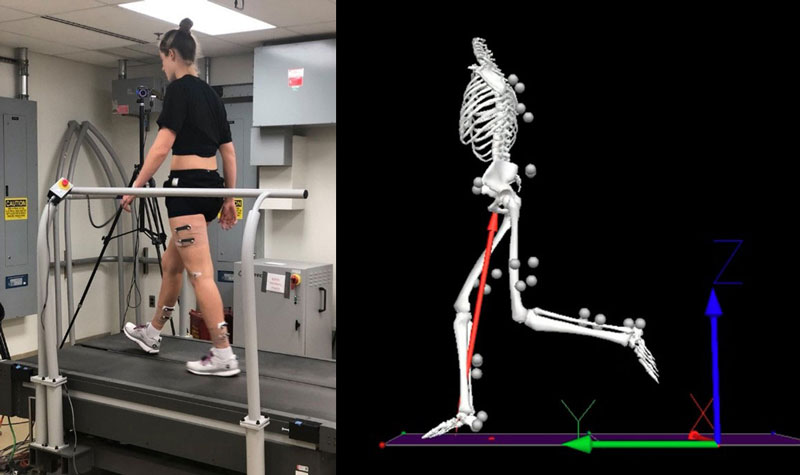
Military service members continue to sustain traumatic anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries at a high rate in training and sports-related activities. The significant lost duty time, poor self-reported functional outcomes, and long-term disability caused by these injuries directly leads to degraded operational readiness and exorbitant costs to both the Military Health System (MHS) and the Department of Veterans Affairs.
March 2021

TATRC has opened the Advanced Medical Technology Initiative (AMTI), formally AMEDD Advanced Medical Technology Initiative (AAMTI) proposal submission process for FY22.
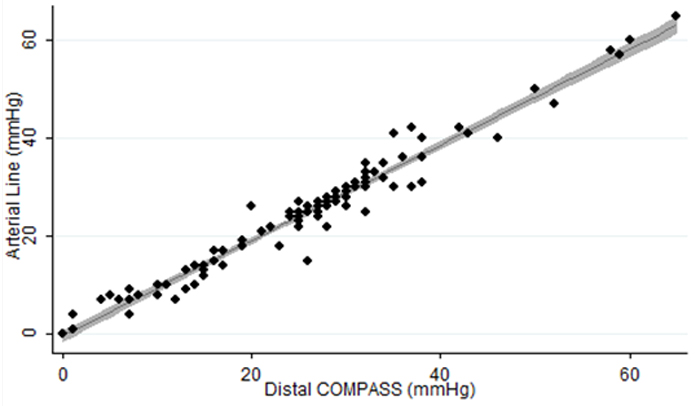
Although there have been great advances in the care of Service Members wounded in combat and other operational environments, bleeding remains a common cause of death. Among deaths that have been determined to be “potentially preventable,” hemorrhage has been identified as the primary cause in 80-90% of cases.
In a typical year, Ms. Holly Pavliscsak, the Advanced Medical Technology Initiative (AMTI) Program Manager (PM) visits two to three military treatment facilities (MTF) on-site and in person where AMTI has active projects to check in with Innovators directly.
December 2020
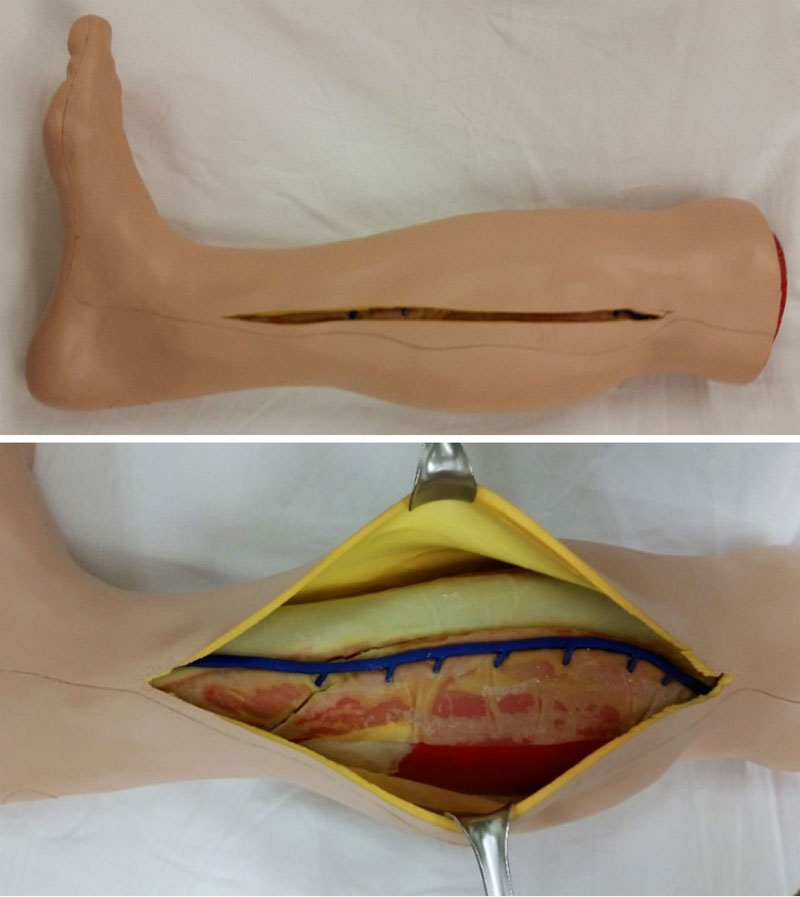
Injuries to the lower leg are very common in combat casualties and one of the frequent consequences of such injuries is increased pressure within the envelope surrounding those muscle groups called Compartment Syndrome (CS).
On 13 November, TATRC’s Advanced Medical Technology Initiative (AMTI) hosted a virtual town hall for the staff at Brooke Army Medical Center (BAMC). This virtual event was led by AMTI Program Manager, Ms. Holly Pavliscsak, who has managed the AMTI since 2016 and has 24 years’ experience in military medical research with an emphasis on medical technology projects and telemedicine.
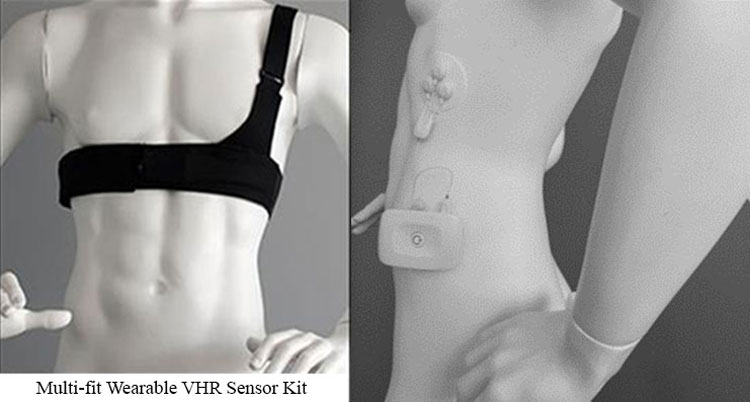
Around 20% of combat casualties from Iraq and Afghanistan have sustained a traumatic brain injury (TBI). Furthermore, Service Members with blast-related injuries often sustain multiple co-occurring disorders, including Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) and other mood disorders, chronic pain, and cognitive dysfunctions.
As with most things in the DoD, change is a common occurrence. In the last year the AMEDD Advanced Medical Technology Initiative (AAMTI) has undergone some big changes of its own.
September 2020

Soldiers encounter a wide range of potentially toxic chemicals throughout their military lifecycle; however, fast and inexpensive toxicity screening of chemicals found in and around military sites is not currently available.
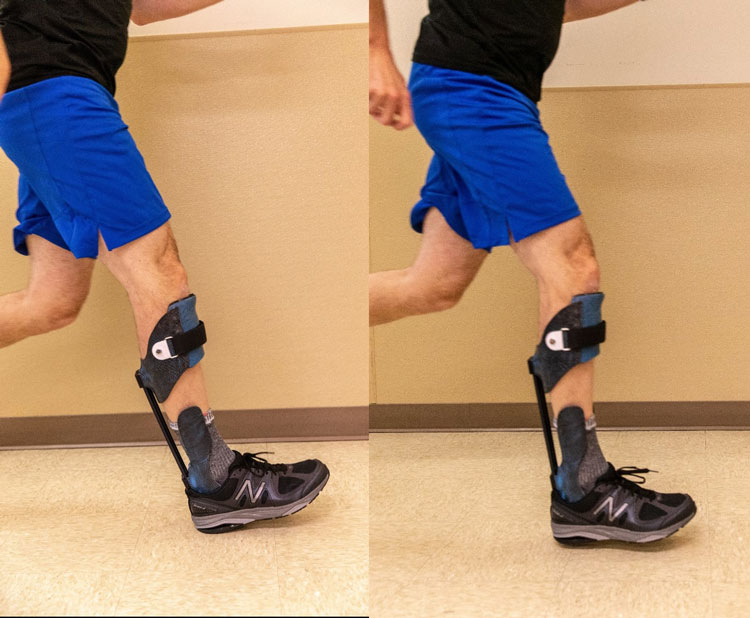
This project is the second in a line of AMTI-funded work using real-time bio-feedback to improve performance and rehabilitation outcomes for Service Members with severe lower extremity injuries. Ankle-foot orthoses are a type of bracing system often prescribed to support and stabilize the ankle and foot of individuals with lower extremity injuries.
June 2020

Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta (REBOA) for hemorrhage control after severe traumatic injury is rapidly gaining use in both civilian trauma centers and in the deployed environment.
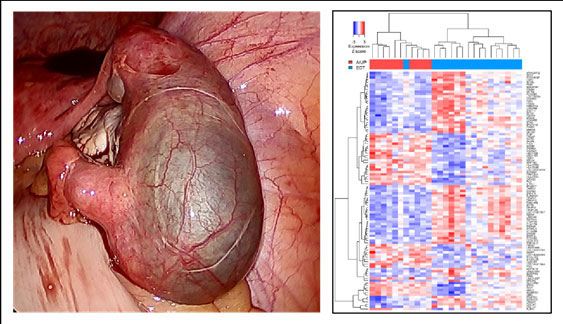
Nearly 16% of active component U.S. military members are women, and the majority are reproductive age. As the number of military servicewomen and their operational scope increase, it is important to understand and mitigate the prevalent health issues that uniquely impact their readiness.
March 2020

Physical therapists regularly evaluate and treat patients with musculoskeletal (MSK) injuries, which is the number one cause of medical non-deployability in military personnel. To effectively treat and manage injuries, physical therapists perform many tests and measures to assess a patient’s function, movement, and other factors that contribute to injury and recovery.
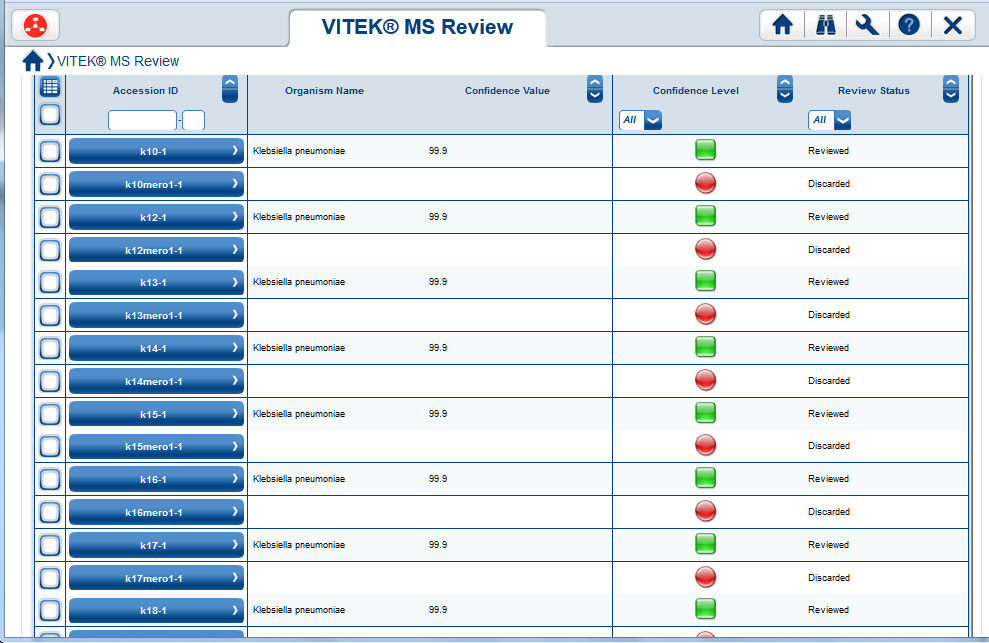
The emergence of antibiotic resistant organisms pose a significant public health concern. The prevalence of antibiotic resistance especially in Gram-negative bacteria continues to increase globally. Since the beginning of Operation Iraqi Freedom and Operation Enduring Freedom, the U.S. military healthcare system has experienced a notable increase in the number of antibiotic-resistant organisms being isolated from wounded Service Members.